# 前导
今天就浅浅学了一下,这玩意比较看运气吧。
声明:我学模拟退火时间不长,很多需要严谨证明的地方,我都没有证明。
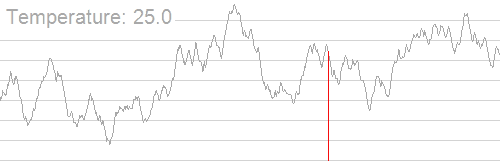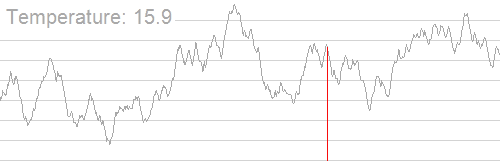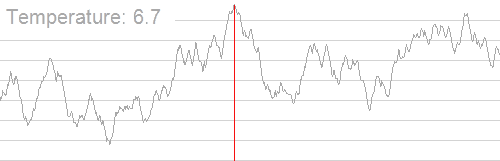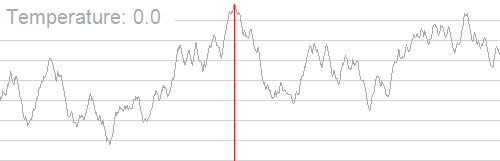
一张图介绍他的运行过程,随着温度的降低,跳跃越来越不随机,最优解也越来越稳定。
# 部分 1
退火算法一般是由两个部分完成的。
第一个是退火主体,找点,因为模拟退火是一个随机化算法,所以他找点也主打一个随机,所以一般模拟退火不只是做一次而是做多次。
Code
void simulate_anneal(){ | |
pair<double,double> cur(rand(0,10000),rand(0,10000));// 当前最优点 | |
for(double t=1e4;t>1e-4;t*=0.99){ | |
pair<double,double> np(rand(cur.first-t,cur.first+t),rand(cur.second-t,cur.second+t));// 随机出来下一个点 | |
double dt=calc(np)-calc(cur);// 比较两个点的贡献 | |
if(exp(-dt/t)>rand(0,1)){// 下面会说 | |
cur=np; | |
} | |
} | |
} |
#
在以上代码中的 是可以利用题目输入的值的平均数,来当第一次时 的坐标,后面几次的 都是拿之前的最优点的坐标当最初坐标。
#
可以理解成一个范围(或者是步长), 也就是从当前最优点的由这个 所划出来的范围中随机下一个点,后面的 0.99 是衰减系数,随着次数的增加, 每乘一次衰减系数,就意味着范围的减小,那么就会趋于稳定,最后选出一个点。 1e-4 是为了 的精度。
温度 T 的初始值设置问题。 初始温度高,则搜索到全局最优解的可能性大,但因此要花费大量的计算时间;反之,则可节约计算时间,但全局搜索性能可能受到影响。
退火速度问题。 模拟退火算法的全局搜索性能也与退火速度密切相关。同一温度下的 “充分” 搜索 (退火) 是相当必要的,但这需要计算时间。
温度管理问题 降温系数应为正的略小于 1.00 的常数。
这三个都根据实际需要进行调试,衰减系数越大衰减的越快,那么次数相对应的也就越少,可能会错过答案,取得区间最优解。
#
就是 ,前面的负号根据情况去掉,当 时 肯定是位于 的。对于一个题目,我们想要求一个最小值,当 时,那么随机出来的点肯定不优,但是在 到这个点的过程中,可能有一个点 ,所以让这个随机出来的点有可能被选,所以代码写成 就是让 时直接替换,当 时有概率替换。当求最大值的时候同理,改一下符号就好,要是这样不好理解的话,可以写成这样:
if(dt<0){ | |
cur=np; | |
}else if(exp(-dt/t)>rand(0,1)){ | |
cur=np; | |
} |
# 部分 2
第二个部分就是主体中的 函数,这一部分没什么好说的,就是根据题目要求解决问题,必要的时候加贪心优化或者分块优化。
double get_dist(pair<double,double> a,pair<double,double> b){ | |
double dx=a.first-b.first; | |
double dy=a.second-b.second; | |
return sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy); | |
} | |
double calc(pair<double,double> p){ | |
double res=0; | |
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ | |
res+=get_dist(p,q[i]); | |
} | |
ans=min(ans,res); | |
return res; | |
} |
一般都是在运行 函数的时候更新答案。
# 部分 3
在 函数中,主要搞一个 卡时,这个是比较有必要的,因为你也不知道评测时的机器能跑多少次模拟退火,所以可以根据运行时间长短来判断是否还要继续模拟退火。
#include<ctime> | |
while ((double)clock()/CLOCKS_PER_SEC < 0.8){ | |
simulate_anneal(); | |
} |
注
在 和 中 的返回时间不一样,一个是毫秒,一个是微秒,所以得加一个 /CLOCKS_PER_SEC 让它把单位换成秒,这样就方便了。
网上有一些随机化种子,大家可以适当参考。
# 例题
搞几道例题。
# 星星还是树
# 题面:
在二维平面上有 个点,第 个点的坐标为 。
请你找出一个点,使得该点到这 个点的距离之和最小。
该点可以选择在平面中的任意位置,甚至与这 个点的位置重合。
# 数据范围:
就是一个求最小值的题目,具有连续性。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
const double MAX_TIME=0.9;
const int MAXN=110;
pair<double,double> q[MAXN];
double ans=1e8;
int n;
double rand(double l,double r){//在l r范围内
return (double)rand()/RAND_MAX*(r-l)+l;
}
double get_dist(pair<double,double> a,pair<double,double> b){
double dx=a.first-b.first;
double dy=a.second-b.second;
return sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy);
}
double calc(pair<double,double> p){//求贡献
double res=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
res+=get_dist(p,q[i]);
}
ans=min(ans,res);
return res;
}
void simulate_anneal(){
pair<double,double> cur(rand(0,10000),rand(0,10000));
for(double t=1e4;t>1e-4;t*=0.99){
pair<double,double> np(rand(cur.first-t,cur.first+t),rand(cur.second-t,cur.second+t));
double dt=calc(np)-calc(cur);
if(exp(-dt/t)>rand(0,1)){//这里自己研究研究
cur=np;
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>q[i].first>>q[i].second;
}
while ((double)clock()/CLOCKS_PER_SEC < MAX_TIME){
simulate_anneal();
}
printf("%.0lf",ans);
}
# 均分数据
# 题面
已知 个正整数 。今要将它们分成 组,使得各组数据的数值和最平均,即各组数字之和的均方差最小。均方差公式如下:
其中 为均方差, 为各组数据和的平均值, 为第 组数据的数值和。
# 数据范围
对于 的数据,保证有 ,
对于 的数据,保证有 ,
这个题需要用的贪心的思想,每一次都让最小的一组加上该数。
代码
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <cstring> | |
#include <cstdio> | |
#include <cmath> | |
#include <map> | |
#include <queue> | |
#include <stack> | |
#include <set> | |
#include <iomanip> | |
#include <ctime> | |
using namespace std; | |
const double TIME_MAXN=0.9; | |
const int MAXN=1e2; | |
int q[MAXN],s[MAXN]; | |
int n,m; | |
double ans=1e8; | |
double calc(){ | |
double res=0; | |
double sum=0; | |
memset(s,0,sizeof(s)); | |
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ | |
int k=1; | |
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ | |
if(s[j]<s[k]){// 让大小最小的一组加上该数 | |
k=j; | |
} | |
} | |
s[k]+=q[i]; | |
} | |
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){// 题目中的公式 | |
sum+=(double)s[i]/m; | |
} | |
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ | |
res+=(s[i]-sum)*(s[i]-sum); | |
} | |
res=sqrt(res/m); | |
ans=min(ans,res); | |
return res; | |
} | |
void simulate_anneal(){ | |
random_shuffle(q+1,q+1+n); | |
for(double t=1e4;t>1e-6;t*=0.995){ | |
int a=rand()%(n+1),b=rand()%(n+1); | |
while(a==0){ | |
a=rand()%(n+1); | |
} | |
while(b==0){ | |
b=rand()%(n+1); | |
} | |
double x=calc(); | |
swap(q[a],q[b]); | |
double y=calc(); | |
double dt=y-x; | |
if(exp(-dt/t)<(double)rand()/RAND_MAX){//y-x 是正的,那么是有概率的 | |
swap(q[a],q[b]); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
int main(){ | |
cin>>n>>m; | |
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ | |
cin>>q[i]; | |
} | |
while((double)clock()/CLOCKS_PER_SEC< TIME_MAXN){ | |
simulate_anneal(); | |
} | |
printf("%.2lf",ans); | |
} |
# 平衡点 / 吊打 XXX
# 题面
如图,有 个重物,每个重物系在一条足够长的绳子上。
每条绳子自上而下穿过桌面上的洞,然后系在一起。图中 处就是公共的绳结。假设绳子是完全弹性的(即不会造成能量损失),桌子足够高(重物不会垂到地上),且忽略所有的摩擦,求绳结 最终平衡于何处。
# 数据范围
桌面上的洞都比绳结 小得多,所以即使某个重物特别重,绳结 也不可能穿过桌面上的洞掉下来,最多是卡在某个洞口处。
根据高中物理,当它最后停在或者是卡在一个点时,那个点一定使得总的重力势能最小的点,可以使系统平衡,即使 最小。
这么看来,这就是一个求最小值的题目啦,但是我总是挂一个点💔,所以我的代码看看就行。
Code
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <cstring> | |
#include <cstdio> | |
#include <cmath> | |
#include <map> | |
#include <queue> | |
#include <stack> | |
#include <set> | |
#include <iomanip> | |
#include <ctime> | |
// #define double long double | |
using namespace std; | |
const int MAXN=1e4+10; | |
const double TIME_MAXN=0.9; | |
int n; | |
struct node{ | |
int x,y,w; | |
}p[MAXN]; | |
struct node2{ | |
double x,y,w=1e12; | |
}ans; | |
double get_dist(pair<double,double>q,node a){ | |
double dx=q.first-a.x; | |
double dy=q.second-a.y; | |
return sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy)*a.w; | |
} | |
double rand(double l,double r){ | |
return (double)rand()/RAND_MAX*(r-l)+l; | |
} | |
double calc(pair<double,double> q){ | |
double res=0; | |
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ | |
res+=get_dist(q,p[i]); | |
} | |
if(res<ans.w){ | |
ans.w=res; | |
ans.x=q.first; | |
ans.y=q.second; | |
} | |
return res; | |
} | |
void simulate_anneal(){ | |
pair<double,double> cur(rand(-10000,10000),rand(-10000,10000)); | |
for(double t=2e5;t>1e-8;t*=0.99){ | |
pair<double,double> np(rand(cur.first-t,cur.first+t),rand(cur.second-t,cur.second+t)); | |
double dt=calc(np)-calc(cur); | |
if(exp(-dt/t)>(double)rand(0,1)){ | |
cur=np; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
int main(){ | |
cin>>n; | |
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ | |
cin>>p[i].x>>p[i].y>>p[i].w; | |
} | |
while((double)clock()/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<TIME_MAXN){ | |
simulate_anneal(); | |
} | |
printf("%.3lf %.3lf",ans.x,ans.y); | |
} |
# 炸弹攻击 1
# 题面
给你 个圆形建筑的位置与半径,给你 个敌人的位置,你有一个毁灭半径最大为 的炸弹,可以这只一个不超过 的范围,然后选择平面上的一个点引爆,且不能破坏建筑,若爆炸半径与某个建筑正好擦边,那也不会破坏建筑,但也会消灭这个边界上的敌人,求满足以上条件最多可以消灭多少敌人。
# 数据范围
;
。
这个题是求最大值,跟前面几道题目不一样,主要需要更改的是 中的 判断语句。
Code
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
#include <cstring> | |
#include <cstdio> | |
#include <cmath> | |
#include <map> | |
#include <queue> | |
#include <stack> | |
#include <set> | |
#include <iomanip> | |
using namespace std; | |
const int MAXN=1e5+10; | |
int n,m,r; | |
struct node{ | |
int x,y,r; | |
}bui[MAXN],ene[MAXN]; | |
double ans=0; | |
double ansx,ansy; | |
double rand(double l,double r){ | |
return (double)rand()/RAND_MAX*(r-l)+l; | |
} | |
double get_dist(pair<double,double> x,node y){ | |
double dx=x.first-y.x; | |
double dy=x.second-y.y; | |
return sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy)-y.r; | |
} | |
double calc(pair<double,double> a){ | |
double res=0; | |
double dis_min=r; | |
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ | |
dis_min=min(dis_min,get_dist(a,bui[i])); | |
} | |
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ | |
if(get_dist(a,ene[j])<=dis_min){ | |
res++; | |
} | |
} | |
ans=max(ans,res); | |
return res; | |
} | |
void simulate_anneal(){ | |
pair<double,double> cur={ansx/m,ansy/m}; | |
for(double t=2e4;t>1e-4;t*=0.996){ | |
pair<double,double> np(rand(cur.first-t,cur.first+t),rand(cur.second-t,cur.second+t)); | |
double dt=calc(np)-calc(cur); | |
if(dt>0){// 像这种分开判断的,也可以在这里更新答案, | |
// 在 calc 中更新也是可以的 | |
cur=np; | |
ansx=cur.first; | |
ansy=cur.second; | |
}else if(exp(-dt/t)*RAND_MAX<rand()){ | |
cur=np; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
int main(){ | |
cin>>n>>m>>r; | |
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ | |
cin>>bui[i].x>>bui[i].y>>bui[i].r; | |
} | |
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ | |
cin>>ene[i].x>>ene[i].y; | |
ansx+=ene[i].x; | |
ansy+=ene[i].y; | |
} | |
// simulate_anneal();/ | |
while((double)clock()/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<0.9){ | |
simulate_anneal(); | |
} | |
cout<<ans; | |
} |
# 结束了?
等有题目再补充吧……